What Is the Product of Radioactive Decay 0-1e Called
The lab finds that the chip contains 5g of carbon and has an activity of 05 Bq. The mass is being converted into energy.

Alpha Decay Beta Decay Gamma Decay Electron Capture Positron Production Nuclear Chemistry Youtube
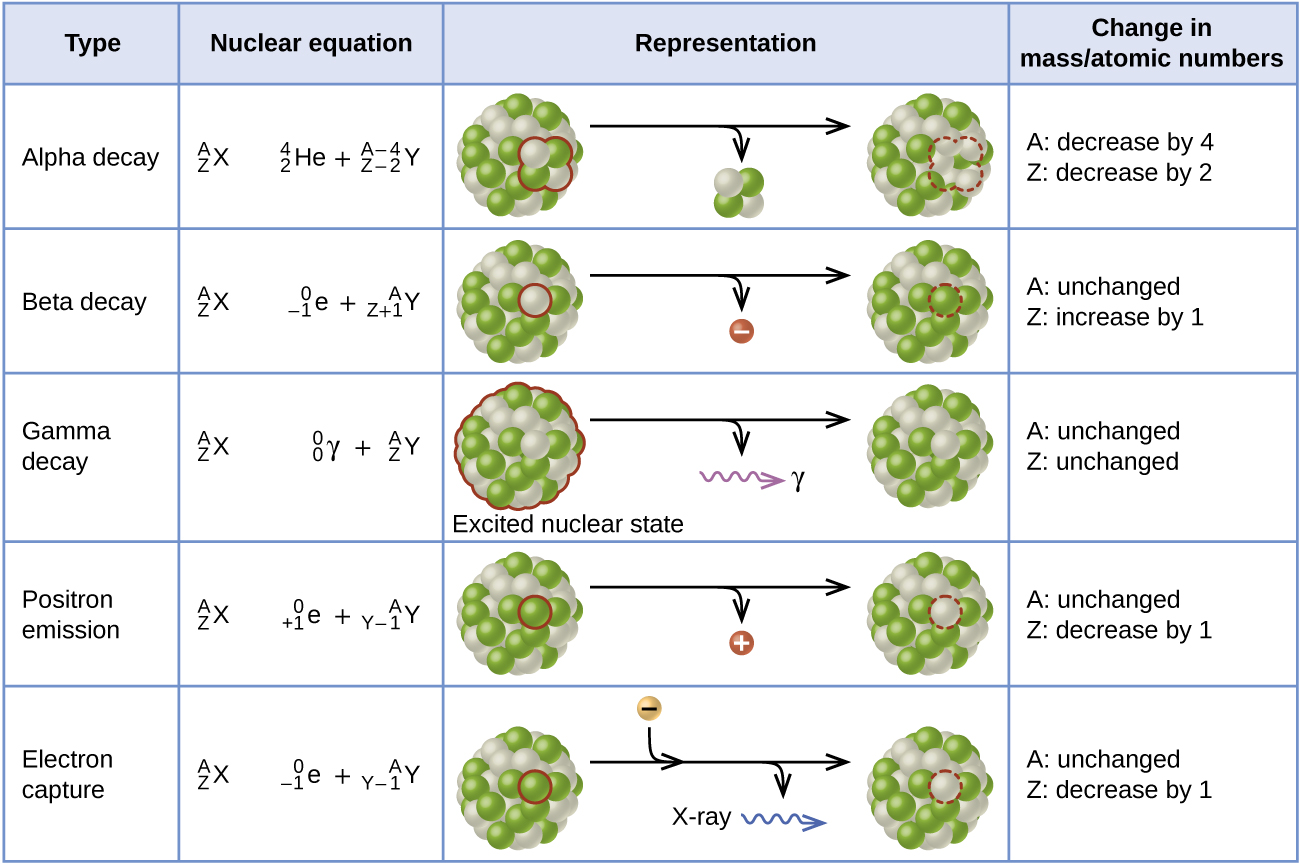
Beta decay is when a nucleus decays spontaneously by emitting an electron or a positron.

. An amateur archeologist finds a bone that she believes to be from a dinosaur and she sends a chip off to a laboratory for 14C dating. The electron captured by the nucleus in this reaction is usually a 1s electron because electrons in this orbital are the closest to the nucleus. The radioactive decay of iodine is shown in the graph.
0 1 2 n. The first crucial radiogenic radionuclide to discuss is 226 Ra T 12 160 10 3 y a decay product of long-lived 230 Th T 12 756 10 4 y which is part of the uranium decay series Fig. It is a radioactive and kills cancer due to its intense gamma ray emission.
And it follows the radioactive laws. The product of a radioactive decay processcalled the daughter of the parent isotopemay itself be unstable in which case it too will decay. What particle is needed to complete the following equation.
Alpha decay beta decay and gamma decay although beta decay in itself comes in three different types. In the equation 14 6 C -- 14 7 N 0 -1 B the _____ decay of radioactive carbon-14 results in the creation of a new nitrogen-14 atom. 146C 147N 0-1e the product nucleus has an atomic number that is one more than that of the original nucleus.
The daughter nuclide may be stable or it may decay itself. Positron emission emission of a positron from an unstable nucleus. Plutonium is converted to uranium.
The process continues until a stable nuclide has been formed. 146C 0-1e 147N. Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction.
A Beta decay can be a beta minus or a beta plus decay. 0060 1 2 n o r nlog2 1 67 w hic give s 40 Thus the time is t nT 1 2 406 5730 yr 23104 yr. 10n 11p 0-1e An example of beta emission is the radioactive decay of carbon-14.
The mass number remains the same. The unstable nuclide is called the parent nuclide. TF- The production of nitrogen-13 and a neutron from boron-10 by bombardment with a helium-4 nucleus is an example of radioactive decay False TF- When Ra-226 undergoes alpha decay an atom of lead is also produced.
What is the product of this radioactive decay. The nature of radioactive emissions. This is also a spontaneous process like the alpha decay with a definite disintegration energy and half-life.
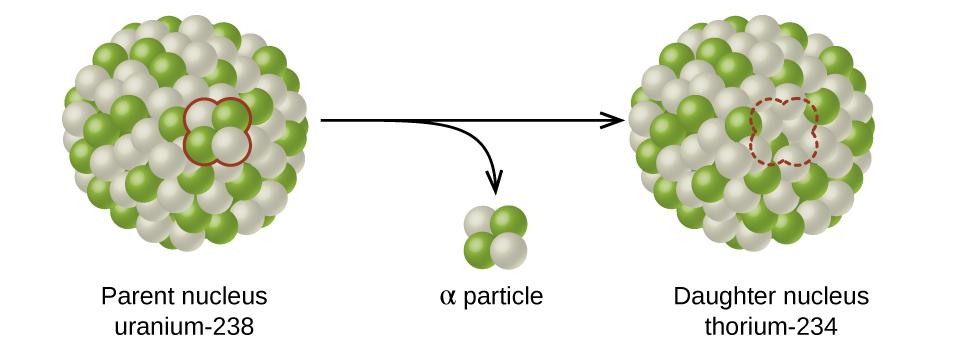
Causes the mass number to decrease by 4 causes the atomic number to decrease by 2. The daughter nuclide may be stable or it may decay itself. Ionizing radiation Radiation with so much energy it can knock electrons out of atoms.
An electron emitted from the nucleus during some kinds of radioactive decay is known as. The spontaneous change of an unstable nuclide into another is radioactive decay. The effect of this decay is that.
The spontaneous change of an unstable nuclide into another is radioactive decay. The nuclide that results from the decay is known as the daughter nuclide. Ionizing radiation can affect the atoms in living things so it poses a health risk by damaging tissue and DNA in genes.
The nuclide that results from the decay is known as the daughter nuclide. To what element does polonium-208 atomic number 84 decay when it emits an alpha particle. 00149 mg The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the time required for one-half of the initial mass to decay into a different element.
The unstable nuclide is called the parent nuclide. What is the effect of this decay. For the most common types of radioactive decay the order of mass from lightest to heaviest is.
23994Pu 42He 23592U. 23992U 42He _____ 10n. The unstable nuclide is called the parent nuclide.
A beta b particle. There are three types of radioactive decay. 9943Tc 9944Ru 0-1e.
Play this game to review Physics. Learning about these forms of nuclear decay is a crucial part of any nuclear physics course. 33 and while it is an almost pure alpha emitter its contribution to the natural radiation exposure is insignificant the opposite can be said.
14-6C 1-1H. Radioactive decay is the emission of energy in the form of. That represents a beta particle.
The spontaneous change of an unstable nuclide into another is radioactive decay. The nuclide that results from the decay is known as the daughter nuclide. The rate of decay of radioactive isotope is called.
Only 3 or 4 atoms of this has ever been made since it is very hard to make. The mass is gained or lost in nuclear reactions Delta mn 1-10 mgmol and mass is a form of energy Emc2 Mass is lost. A third form of beta decay is called positron sup emission.
Loss of an alpha particle. A beta particle _-1colorwhiteaa0beta is simply a high-speed electronWhen a radioactive nuclide undergoes beta minus decay a neutron located inside its nucleus is being converted into a proton. The positron is the antimatter equivalent of an electron.
The daughter nuclide may be stable or it may decay itself. But most of the time when nuclei change to a lower energy state in nature its down to radioactive decay. The product of this reaction can be predicted once again by assuming that mass and charge are conserved.
What is the product of radioactive decay 0 -1e called.
21 3 Radioactive Decay Chemistry
Comments
Post a Comment